Window that can serve as a target for 2D drawing. More...
#include <SFML/Graphics/RenderWindow.hpp>
Public Member Functions | |
| RenderWindow ()=default | |
| Default constructor. | |
| RenderWindow (VideoMode mode, const String &title, std::uint32_t style=Style::Default, State state=State::Windowed, const ContextSettings &settings={}) | |
| Construct a new window. | |
| RenderWindow (VideoMode mode, const String &title, State state, const ContextSettings &settings={}) | |
| Construct a new window. | |
| RenderWindow (WindowHandle handle, const ContextSettings &settings={}) | |
| Construct the window from an existing control. | |
| Vector2u | getSize () const override |
| Get the size of the rendering region of the window. | |
| void | setIcon (const Image &icon) |
| Change the window's icon. | |
| bool | isSrgb () const override |
| Tell if the window will use sRGB encoding when drawing on it. | |
| bool | setActive (bool active=true) override |
| Activate or deactivate the window as the current target for OpenGL rendering. | |
| void | create (VideoMode mode, const String &title, std::uint32_t style=Style::Default, State state=State::Windowed) override |
| Create (or recreate) the window. | |
| virtual void | create (VideoMode mode, const String &title, std::uint32_t style, State state, const ContextSettings &settings) |
| Create (or recreate) the window. | |
| void | create (VideoMode mode, const String &title, State state) override |
| Create (or recreate) the window. | |
| virtual void | create (VideoMode mode, const String &title, State state, const ContextSettings &settings) |
| Create (or recreate) the window. | |
| void | create (WindowHandle handle) override |
| Create (or recreate) the window from an existing control. | |
| virtual void | create (WindowHandle handle, const ContextSettings &settings) |
| Create (or recreate) the window from an existing control. | |
| void | close () override |
| Close the window and destroy all the attached resources. | |
| const ContextSettings & | getSettings () const |
| Get the settings of the OpenGL context of the window. | |
| void | setVerticalSyncEnabled (bool enabled) |
| Enable or disable vertical synchronization. | |
| void | setFramerateLimit (unsigned int limit) |
| Limit the framerate to a maximum fixed frequency. | |
| bool | setActive (bool active=true) const |
| Activate or deactivate the window as the current target for OpenGL rendering. | |
| void | display () |
| Display on screen what has been rendered to the window so far. | |
| bool | isOpen () const |
| Tell whether or not the window is open. | |
| std::optional< Event > | pollEvent () |
| Pop the next event from the front of the FIFO event queue, if any, and return it. | |
| std::optional< Event > | waitEvent (Time timeout=Time::Zero) |
| Wait for an event and return it. | |
| template<typename... Ts> | |
| void | handleEvents (Ts &&... handlers) |
| Handle all pending events. | |
| Vector2i | getPosition () const |
| Get the position of the window. | |
| void | setPosition (Vector2i position) |
| Change the position of the window on screen. | |
| void | setSize (Vector2u size) |
| Change the size of the rendering region of the window. | |
| void | setMinimumSize (const std::optional< Vector2u > &minimumSize) |
| Set the minimum window rendering region size. | |
| void | setMaximumSize (const std::optional< Vector2u > &maximumSize) |
| Set the maximum window rendering region size. | |
| void | setTitle (const String &title) |
| Change the title of the window. | |
| void | setIcon (Vector2u size, const std::uint8_t *pixels) |
| Change the window's icon. | |
| void | setVisible (bool visible) |
| Show or hide the window. | |
| void | setMouseCursorVisible (bool visible) |
| Show or hide the mouse cursor. | |
| void | setMouseCursorGrabbed (bool grabbed) |
| Grab or release the mouse cursor. | |
| void | setMouseCursor (const Cursor &cursor) |
| Set the displayed cursor to a native system cursor. | |
| void | setKeyRepeatEnabled (bool enabled) |
| Enable or disable automatic key-repeat. | |
| void | setJoystickThreshold (float threshold) |
| Change the joystick threshold. | |
| void | requestFocus () |
| Request the current window to be made the active foreground window. | |
| bool | hasFocus () const |
| Check whether the window has the input focus. | |
| WindowHandle | getNativeHandle () const |
| Get the OS-specific handle of the window. | |
| bool | createVulkanSurface (const VkInstance &instance, VkSurfaceKHR &surface, const VkAllocationCallbacks *allocator=nullptr) |
| Create a Vulkan rendering surface. | |
| void | clear (Color color=Color::Black) |
| Clear the entire target with a single color. | |
| void | clear (Color color, StencilValue stencilValue) |
| Clear the entire target with a single color and stencil value. | |
| void | clearStencil (StencilValue stencilValue) |
| Clear the stencil buffer to a specific value. | |
| void | setView (const View &view) |
| Change the current active view. | |
| const View & | getView () const |
| Get the view currently in use in the render target. | |
| const View & | getDefaultView () const |
| Get the default view of the render target. | |
| IntRect | getViewport (const View &view) const |
| Get the viewport of a view, applied to this render target. | |
| IntRect | getScissor (const View &view) const |
| Get the scissor rectangle of a view, applied to this render target. | |
| Vector2f | mapPixelToCoords (Vector2i point) const |
| Convert a point from target coordinates to world coordinates, using the current view. | |
| Vector2f | mapPixelToCoords (Vector2i point, const View &view) const |
| Convert a point from target coordinates to world coordinates. | |
| Vector2i | mapCoordsToPixel (Vector2f point) const |
| Convert a point from world coordinates to target coordinates, using the current view. | |
| Vector2i | mapCoordsToPixel (Vector2f point, const View &view) const |
| Convert a point from world coordinates to target coordinates. | |
| void | draw (const Drawable &drawable, const RenderStates &states=RenderStates::Default) |
| Draw a drawable object to the render target. | |
| void | draw (const Vertex *vertices, std::size_t vertexCount, PrimitiveType type, const RenderStates &states=RenderStates::Default) |
| Draw primitives defined by an array of vertices. | |
| void | draw (const VertexBuffer &vertexBuffer, const RenderStates &states=RenderStates::Default) |
| Draw primitives defined by a vertex buffer. | |
| void | draw (const VertexBuffer &vertexBuffer, std::size_t firstVertex, std::size_t vertexCount, const RenderStates &states=RenderStates::Default) |
| Draw primitives defined by a vertex buffer. | |
| void | pushGLStates () |
| Save the current OpenGL render states and matrices. | |
| void | popGLStates () |
| Restore the previously saved OpenGL render states and matrices. | |
| void | resetGLStates () |
| Reset the internal OpenGL states so that the target is ready for drawing. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| void | onCreate () override |
| Function called after the window has been created. | |
| void | onResize () override |
| Function called after the window has been resized. | |
| void | initialize () |
| Performs the common initialization step after creation. | |
Detailed Description
Window that can serve as a target for 2D drawing.
sf::RenderWindow is the main class of the Graphics module.
It defines an OS window that can be painted using the other classes of the graphics module.
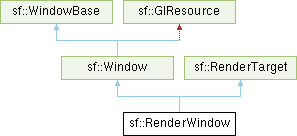
sf::RenderWindow is derived from sf::Window, thus it inherits all its features: events, window management, OpenGL rendering, etc. See the documentation of sf::Window for a more complete description of all these features, as well as code examples.
On top of that, sf::RenderWindow adds more features related to 2D drawing with the graphics module (see its base class sf::RenderTarget for more details). Here is a typical rendering and event loop with a sf::RenderWindow:
Like sf::Window, sf::RenderWindow is still able to render direct OpenGL stuff. It is even possible to mix together OpenGL calls and regular SFML drawing commands.
- See also
sf::Window,sf::RenderTarget,sf::RenderTexture,sf::View
Definition at line 54 of file RenderWindow.hpp.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ RenderWindow() [1/4]
|
default |
Default constructor.
This constructor doesn't actually create the window, use the other constructors or call create() to do so.
◆ RenderWindow() [2/4]
| sf::RenderWindow::RenderWindow | ( | VideoMode | mode, |
| const String & | title, | ||
| std::uint32_t | style = Style::Default, | ||
| State | state = State::Windowed, | ||
| const ContextSettings & | settings = {} ) |
Construct a new window.
This constructor creates the window with the size and pixel depth defined in mode. An optional style can be passed to customize the look and behavior of the window (borders, title bar, resizable, closable, ...).
The last parameter is an optional structure specifying advanced OpenGL context settings such as anti-aliasing, depth-buffer bits, etc. You shouldn't care about these parameters for a regular usage of the graphics module.
- Parameters
-
mode Video mode to use (defines the width, height and depth of the rendering area of the window) title Title of the window style Window style, a bitwise OR combination of sf::Styleenumeratorsstate Window state settings Additional settings for the underlying OpenGL context
◆ RenderWindow() [3/4]
| sf::RenderWindow::RenderWindow | ( | VideoMode | mode, |
| const String & | title, | ||
| State | state, | ||
| const ContextSettings & | settings = {} ) |
Construct a new window.
This constructor creates the window with the size and pixel depth defined in mode. If state is State::Fullscreen, then mode must be a valid video mode.
The last parameter is an optional structure specifying advanced OpenGL context settings such as anti-aliasing, depth-buffer bits, etc.
- Parameters
-
mode Video mode to use (defines the width, height and depth of the rendering area of the window) title Title of the window state Window state settings Additional settings for the underlying OpenGL context
◆ RenderWindow() [4/4]
|
explicit |
Construct the window from an existing control.
Use this constructor if you want to create an SFML rendering area into an already existing control.
The second parameter is an optional structure specifying advanced OpenGL context settings such as anti-aliasing, depth-buffer bits, etc. You shouldn't care about these parameters for a regular usage of the graphics module.
- Parameters
-
handle Platform-specific handle of the control (HWND on Windows, Window on Linux/FreeBSD, NSWindow on macOS) settings Additional settings for the underlying OpenGL context
Member Function Documentation
◆ clear() [1/2]
|
inherited |
Clear the entire target with a single color and stencil value.
The specified stencil value is truncated to the bit width of the current stencil buffer.
- Parameters
-
color Fill color to use to clear the render target stencilValue Stencil value to clear to
◆ clear() [2/2]
|
inherited |
Clear the entire target with a single color.
This function is usually called once every frame, to clear the previous contents of the target.
- Parameters
-
color Fill color to use to clear the render target
◆ clearStencil()
|
inherited |
Clear the stencil buffer to a specific value.
The specified value is truncated to the bit width of the current stencil buffer.
- Parameters
-
stencilValue Stencil value to clear to
◆ close()
|
overridevirtualinherited |
Close the window and destroy all the attached resources.
After calling this function, the sf::Window instance remains valid and you can call create() to recreate the window. All other functions such as pollEvent() or display() will still work (i.e. you don't have to test isOpen() every time), and will have no effect on closed windows.
Reimplemented from sf::WindowBase.
◆ create() [1/6]
|
overridevirtualinherited |
Create (or recreate) the window.
If the window was already created, it closes it first. If state is State::Fullscreen, then mode must be a valid video mode.
- Parameters
-
mode Video mode to use (defines the width, height and depth of the rendering area of the window) title Title of the window state Window state
Reimplemented from sf::WindowBase.
◆ create() [2/6]
|
virtualinherited |
Create (or recreate) the window.
If the window was already created, it closes it first. If state is State::Fullscreen, then mode must be a valid video mode.
The last parameter is a structure specifying advanced OpenGL context settings such as anti-aliasing, depth-buffer bits, etc.
- Parameters
-
mode Video mode to use (defines the width, height and depth of the rendering area of the window) title Title of the window state Window state settings Additional settings for the underlying OpenGL context
◆ create() [3/6]
|
virtualinherited |
Create (or recreate) the window.
If the window was already created, it closes it first. If state is State::Fullscreen, then mode must be a valid video mode.
The last parameter is a structure specifying advanced OpenGL context settings such as anti-aliasing, depth-buffer bits, etc.
- Parameters
-
mode Video mode to use (defines the width, height and depth of the rendering area of the window) title Title of the window style Window style, a bitwise OR combination of sf::Styleenumeratorsstate Window state settings Additional settings for the underlying OpenGL context
◆ create() [4/6]
|
overridevirtualinherited |
Create (or recreate) the window.
If the window was already created, it closes it first. If state is State::Fullscreen, then mode must be a valid video mode.
- Parameters
-
mode Video mode to use (defines the width, height and depth of the rendering area of the window) title Title of the window style Window style, a bitwise OR combination of sf::Styleenumeratorsstate Window state
Reimplemented from sf::WindowBase.
◆ create() [5/6]
|
overridevirtualinherited |
Create (or recreate) the window from an existing control.
Use this function if you want to create an OpenGL rendering area into an already existing control. If the window was already created, it closes it first.
- Parameters
-
handle Platform-specific handle of the control
Reimplemented from sf::WindowBase.
◆ create() [6/6]
|
virtualinherited |
Create (or recreate) the window from an existing control.
Use this function if you want to create an OpenGL rendering area into an already existing control. If the window was already created, it closes it first.
The second parameter is an optional structure specifying advanced OpenGL context settings such as anti-aliasing, depth-buffer bits, etc.
- Parameters
-
handle Platform-specific handle of the control settings Additional settings for the underlying OpenGL context
◆ createVulkanSurface()
|
nodiscardinherited |
◆ display()
|
inherited |
Display on screen what has been rendered to the window so far.
This function is typically called after all OpenGL rendering has been done for the current frame, in order to show it on screen.
◆ draw() [1/4]
|
inherited |
Draw a drawable object to the render target.
- Parameters
-
drawable Object to draw states Render states to use for drawing
◆ draw() [2/4]
|
inherited |
Draw primitives defined by an array of vertices.
- Parameters
-
vertices Pointer to the vertices vertexCount Number of vertices in the array type Type of primitives to draw states Render states to use for drawing
◆ draw() [3/4]
|
inherited |
Draw primitives defined by a vertex buffer.
- Parameters
-
vertexBuffer Vertex buffer states Render states to use for drawing
◆ draw() [4/4]
|
inherited |
Draw primitives defined by a vertex buffer.
- Parameters
-
vertexBuffer Vertex buffer firstVertex Index of the first vertex to render vertexCount Number of vertices to render states Render states to use for drawing
◆ getDefaultView()
|
nodiscardinherited |
◆ getNativeHandle()
|
nodiscardinherited |
Get the OS-specific handle of the window.
The type of the returned handle is sf::WindowHandle, which is a type alias to the handle type defined by the OS. You shouldn't need to use this function, unless you have very specific stuff to implement that SFML doesn't support, or implement a temporary workaround until a bug is fixed.
- Returns
- System handle of the window
◆ getPosition()
|
nodiscardinherited |
◆ getScissor()
Get the scissor rectangle of a view, applied to this render target.
The scissor rectangle is defined in the view as a ratio. This function simply applies this ratio to the current dimensions of the render target to calculate the pixels rectangle that the scissor rectangle actually covers in the target.
- Parameters
-
view The view for which we want to compute the scissor rectangle
- Returns
- Scissor rectangle, expressed in pixels
◆ getSettings()
|
nodiscardinherited |
Get the settings of the OpenGL context of the window.
Note that these settings may be different from what was passed to the constructor or the create() function, if one or more settings were not supported. In this case, SFML chose the closest match.
- Returns
- Structure containing the OpenGL context settings
◆ getSize()
|
nodiscardoverridevirtual |
Get the size of the rendering region of the window.
The size doesn't include the titlebar and borders of the window.
- Returns
- Size in pixels
Implements sf::RenderTarget.
◆ getView()
|
nodiscardinherited |
Get the view currently in use in the render target.
- Returns
- The view object that is currently used
- See also
setView,getDefaultView
◆ getViewport()
Get the viewport of a view, applied to this render target.
The viewport is defined in the view as a ratio, this function simply applies this ratio to the current dimensions of the render target to calculate the pixels rectangle that the viewport actually covers in the target.
- Parameters
-
view The view for which we want to compute the viewport
- Returns
- Viewport rectangle, expressed in pixels
◆ handleEvents()
|
inherited |
Handle all pending events.
This function is not blocking: if there's no pending event then it will return without calling any of the handlers.
This function can take a variadic list of event handlers that each take a concrete event type as a single parameter. The event handlers can be any kind of callable object that has an operator() defined for a specific event type. Additionally a generic callable can also be provided that will be invoked for every event type. If both types of callables are provided, the callables taking concrete event types will be preferred over the generic callable by overload resolution. Generic callables can be used to customize handler dispatching based on the deduced type of the event and other information available at compile time.
Examples of callables:
- Lambda expressions:
[&](const sf::Event::KeyPressed) { ... } - Free functions:
void handler(const sf::Event::KeyPressed&) { ... }
Calling member functions is supported through lambda expressions.
- Parameters
-
handlers A variadic list of callables that take a specific event as their only parameter
◆ hasFocus()
|
nodiscardinherited |
Check whether the window has the input focus.
At any given time, only one window may have the input focus to receive input events such as keystrokes or most mouse events.
- Returns
trueif window has focus,falseotherwise
- See also
requestFocus
◆ initialize()
|
protectedinherited |
Performs the common initialization step after creation.
The derived classes must call this function after the target is created and ready for drawing.
◆ isOpen()
|
nodiscardinherited |
Tell whether or not the window is open.
This function returns whether or not the window exists. Note that a hidden window (setVisible(false)) is open (therefore this function would return true).
- Returns
trueif the window is open,falseif it has been closed
◆ isSrgb()
|
nodiscardoverridevirtual |
Tell if the window will use sRGB encoding when drawing on it.
You can request sRGB encoding for a window by having the sRgbCapable flag set in the ContextSettings
- Returns
trueif the window use sRGB encoding,falseotherwise
Reimplemented from sf::RenderTarget.
◆ mapCoordsToPixel() [1/2]
Convert a point from world coordinates to target coordinates, using the current view.
This function is an overload of the mapCoordsToPixel function that implicitly uses the current view. It is equivalent to:
- Parameters
-
point Point to convert
- Returns
- The converted point, in target coordinates (pixels)
- See also
mapPixelToCoords
◆ mapCoordsToPixel() [2/2]
|
nodiscardinherited |
Convert a point from world coordinates to target coordinates.
This function finds the pixel of the render target that matches the given 2D point. In other words, it goes through the same process as the graphics card, to compute the final position of a rendered point.
Initially, both coordinate systems (world units and target pixels) match perfectly. But if you define a custom view or resize your render target, this assertion is not true anymore, i.e. a point located at (150, 75) in your 2D world may map to the pixel (10, 50) of your render target – if the view is translated by (140, 25).
This version uses a custom view for calculations, see the other overload of the function if you want to use the current view of the render target.
- Parameters
-
point Point to convert view The view to use for converting the point
- Returns
- The converted point, in target coordinates (pixels)
- See also
mapPixelToCoords
◆ mapPixelToCoords() [1/2]
Convert a point from target coordinates to world coordinates, using the current view.
This function is an overload of the mapPixelToCoords function that implicitly uses the current view. It is equivalent to:
- Parameters
-
point Pixel to convert
- Returns
- The converted point, in "world" coordinates
- See also
mapCoordsToPixel
◆ mapPixelToCoords() [2/2]
|
nodiscardinherited |
Convert a point from target coordinates to world coordinates.
This function finds the 2D position that matches the given pixel of the render target. In other words, it does the inverse of what the graphics card does, to find the initial position of a rendered pixel.
Initially, both coordinate systems (world units and target pixels) match perfectly. But if you define a custom view or resize your render target, this assertion is not true anymore, i.e. a point located at (10, 50) in your render target may map to the point (150, 75) in your 2D world – if the view is translated by (140, 25).
For render-windows, this function is typically used to find which point (or object) is located below the mouse cursor.
This version uses a custom view for calculations, see the other overload of the function if you want to use the current view of the render target.
- Parameters
-
point Pixel to convert view The view to use for converting the point
- Returns
- The converted point, in "world" units
- See also
mapCoordsToPixel
◆ onCreate()
|
overrideprotectedvirtual |
Function called after the window has been created.
This function is called so that derived classes can perform their own specific initialization as soon as the window is created.
Reimplemented from sf::WindowBase.
◆ onResize()
|
overrideprotectedvirtual |
Function called after the window has been resized.
This function is called so that derived classes can perform custom actions when the size of the window changes.
Reimplemented from sf::WindowBase.
◆ pollEvent()
|
nodiscardinherited |
Pop the next event from the front of the FIFO event queue, if any, and return it.
This function is not blocking: if there's no pending event then it will return a std::nullopt. Note that more than one event may be present in the event queue, thus you should always call this function in a loop to make sure that you process every pending event.
- Returns
- The event, otherwise
std::nulloptif no events are pending
- See also
waitEvent,handleEvents
◆ popGLStates()
|
inherited |
Restore the previously saved OpenGL render states and matrices.
See the description of pushGLStates to get a detailed description of these functions.
- See also
pushGLStates
◆ pushGLStates()
|
inherited |
Save the current OpenGL render states and matrices.
This function can be used when you mix SFML drawing and direct OpenGL rendering. Combined with popGLStates, it ensures that:
- SFML's internal states are not messed up by your OpenGL code
- your OpenGL states are not modified by a call to a SFML function
More specifically, it must be used around code that calls draw functions. Example:
Note that this function is quite expensive: it saves all the possible OpenGL states and matrices, even the ones you don't care about. Therefore it should be used wisely. It is provided for convenience, but the best results will be achieved if you handle OpenGL states yourself (because you know which states have really changed, and need to be saved and restored). Take a look at the resetGLStates function if you do so.
- See also
popGLStates
◆ requestFocus()
|
inherited |
Request the current window to be made the active foreground window.
At any given time, only one window may have the input focus to receive input events such as keystrokes or mouse events. If a window requests focus, it only hints to the operating system, that it would like to be focused. The operating system is free to deny the request. This is not to be confused with setActive().
- See also
hasFocus
◆ resetGLStates()
|
inherited |
Reset the internal OpenGL states so that the target is ready for drawing.
This function can be used when you mix SFML drawing and direct OpenGL rendering, if you choose not to use pushGLStates/popGLStates. It makes sure that all OpenGL states needed by SFML are set, so that subsequent draw() calls will work as expected.
Example:
◆ setActive() [1/2]
|
nodiscardoverridevirtual |
Activate or deactivate the window as the current target for OpenGL rendering.
A window is active only on the current thread, if you want to make it active on another thread you have to deactivate it on the previous thread first if it was active. Only one window can be active on a thread at a time, thus the window previously active (if any) automatically gets deactivated. This is not to be confused with requestFocus().
- Parameters
-
active trueto activate,falseto deactivate
- Returns
trueif operation was successful,falseotherwise
Reimplemented from sf::RenderTarget.
◆ setActive() [2/2]
|
nodiscardinherited |
Activate or deactivate the window as the current target for OpenGL rendering.
A window is active only on the current thread, if you want to make it active on another thread you have to deactivate it on the previous thread first if it was active. Only one window can be active on a thread at a time, thus the window previously active (if any) automatically gets deactivated. This is not to be confused with requestFocus().
- Parameters
-
active trueto activate,falseto deactivate
- Returns
trueif operation was successful,falseotherwise
◆ setFramerateLimit()
|
inherited |
Limit the framerate to a maximum fixed frequency.
If a limit is set, the window will use a small delay after each call to display() to ensure that the current frame lasted long enough to match the framerate limit. SFML will try to match the given limit as much as it can, but since it internally uses sf::sleep, whose precision depends on the underlying OS, the results may be a little imprecise as well (for example, you can get 65 FPS when requesting 60).
- Parameters
-
limit Framerate limit, in frames per seconds (use 0 to disable limit)
◆ setIcon() [1/2]
| void sf::RenderWindow::setIcon | ( | const Image & | icon | ) |
Change the window's icon.
The OS default icon is used by default.
- Parameters
-
icon Image to use as the icon. The image is copied, so you need not keep the source alive after calling this function.
◆ setIcon() [2/2]
|
inherited |
Change the window's icon.
pixels must be an array of size pixels in 32-bits RGBA format.
The OS default icon is used by default.
- Parameters
-
size Icon's width and height, in pixels pixels Pointer to the array of pixels in memory. The pixels are copied, so you need not keep the source alive after calling this function.
- See also
setTitle
◆ setJoystickThreshold()
|
inherited |
Change the joystick threshold.
The joystick threshold is the value below which no JoystickMoved event will be generated.
The threshold value is 0.1 by default.
- Parameters
-
threshold New threshold, in the range [0, 100]
◆ setKeyRepeatEnabled()
|
inherited |
Enable or disable automatic key-repeat.
If key repeat is enabled, you will receive repeated KeyPressed events while keeping a key pressed. If it is disabled, you will only get a single event when the key is pressed.
Key repeat is enabled by default.
- Parameters
-
enabled trueto enable,falseto disable
◆ setMaximumSize()
|
inherited |
Set the maximum window rendering region size.
Pass std::nullopt to unset the maximum size
- Parameters
-
maximumSize New maximum size, in pixels
◆ setMinimumSize()
|
inherited |
Set the minimum window rendering region size.
Pass std::nullopt to unset the minimum size
- Parameters
-
minimumSize New minimum size, in pixels
◆ setMouseCursor()
|
inherited |
Set the displayed cursor to a native system cursor.
Upon window creation, the arrow cursor is used by default.
- Warning
- The cursor must not be destroyed while in use by the window.
- Features related to Cursor are not supported on iOS and Android.
- Parameters
-
cursor Native system cursor type to display
◆ setMouseCursorGrabbed()
|
inherited |
Grab or release the mouse cursor.
If set, grabs the mouse cursor inside this window's client area so it may no longer be moved outside its bounds. Note that grabbing is only active while the window has focus.
- Parameters
-
grabbed trueto enable,falseto disable
◆ setMouseCursorVisible()
|
inherited |
Show or hide the mouse cursor.
The mouse cursor is visible by default.
- Warning
- On Windows, this function needs to be called from the thread that created the window.
- Parameters
-
visible trueto show the mouse cursor,falseto hide it
◆ setPosition()
|
inherited |
Change the position of the window on screen.
This function only works for top-level windows (i.e. it will be ignored for windows created from the handle of a child window/control).
- Parameters
-
position New position, in pixels
- See also
getPosition
◆ setSize()
|
inherited |
Change the size of the rendering region of the window.
- Parameters
-
size New size, in pixels
- See also
getSize
◆ setTitle()
|
inherited |
◆ setVerticalSyncEnabled()
|
inherited |
Enable or disable vertical synchronization.
Activating vertical synchronization will limit the number of frames displayed to the refresh rate of the monitor. This can avoid some visual artifacts, and limit the framerate to a good value (but not constant across different computers).
Vertical synchronization is disabled by default.
- Parameters
-
enabled trueto enable v-sync,falseto deactivate it
◆ setView()
|
inherited |
Change the current active view.
The view is like a 2D camera, it controls which part of the 2D scene is visible, and how it is viewed in the render target. The new view will affect everything that is drawn, until another view is set. The render target keeps its own copy of the view object, so it is not necessary to keep the original one alive after calling this function. To restore the original view of the target, you can pass the result of getDefaultView() to this function.
- Parameters
-
view New view to use
- See also
getView,getDefaultView
◆ setVisible()
|
inherited |
Show or hide the window.
The window is shown by default.
- Parameters
-
visible trueto show the window,falseto hide it
◆ waitEvent()
|
nodiscardinherited |
Wait for an event and return it.
This function is blocking: if there's no pending event then it will wait until an event is received or until the provided timeout elapses. Only if an error or a timeout occurs the returned event will be std::nullopt. This function is typically used when you have a thread that is dedicated to events handling: you want to make this thread sleep as long as no new event is received.
- Parameters
-
timeout Maximum time to wait ( Time::Zerofor infinite)
- Returns
- The event, otherwise
std::nullopton timeout or if window was closed
- See also
pollEvent,handleEvents
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file: